Introduction
Managing and troubleshooting Kubernetes clusters is hard. Kubernetes is powerful but complex and finding the root cause of issues requires deep expertise and experience. Enter HolmesGPT, an open source on-call DevOps agent that uses AI to simplify the troubleshooting process. Built by Robusta, HolmesGPT goes beyond traditional Kubernetes troubleshooting and integrates with many DevOps tools to streamline incident management. This post will walk you through HolmesGPT, its features, installation and demo it in real world scenarios.
Video
Below is a video demonstration.
Video Chapters
- 00:00 Introduction
- 00:24 What is HolmesGPT?
- 02:45 Demo – Scenario 1
- 08:08 Demo – Scenario 2
- 12:06 Demo – Scenario 3
What is HolmesGPT?
HolmesGPT, according to its GitHub page, is an open source on-call DevOps agent that uses AI to help you investigate and resolve alerts in your infrastructure. It can integrate with many incident management systems like PagerDuty, OpsGenie and monitoring tools like Prometheus, to provide automated analysis and troubleshooting suggestions.
HolmesGPT Features:
- AI Powered Incident Investigation: HolmesGPT can investigate incidents reported by PagerDuty, OpsGenie and other monitoring tools. It automates diagnosing issues, making finding the root cause and potential solutions easier.
- Troubleshooting and Log Analysis: The tool can analyze logs, troubleshoot Prometheus alerts and investigate issues reported in JIRA tickets or GitHub issues. It’s a versatile tool in a DevOps engineer’s toolbox.
- Custom Tools and Runbooks: HolmesGPT can be customized with specific tools and runbooks, so it can access data like traces, APM data or custom APIs that it wouldn’t normally have access to. This makes it provide more accurate and context aware solutions.
- Open Source and Extensible: HolmesGPT is open source and released under the MIT license, so it’s available to everyone. It can be tailored to your needs, making it a flexible tool for any environment.
- Integration with OpenAI: HolmesGPT can integrate with OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock or even a self hosted Large Language Model (LLM). This allows the tool to use advanced AI capabilities to boost its diagnostic power.
Robusta, the company behind HolmesGPT, also offer a SaaS version with a more polished UI and features for managing Kubernetes clusters and alerts. In this post we will see both in action for Kubernetes troubleshooting.
Getting started with HolmesGPT: Installation and Setup
Installing HolmesGPT is easy and the tool supports multiple installation methods. Here’s a quick guide to get you started:
- Prerequisites: You have a Kubernetes cluster running and access to the command-line interface (CLI). You’ll also need an OpenAI API key if you plan to use OpenAI.
- Installation: HolmesGPT can be installed with brew. Or you can use other methods as documented on the GitHub page.
- Configuration: After installation, HolmesGPT needs to be configured to connect to your AI service (e.g. OpenAI) and integrated with your incident management tools (PagerDuty, OpsGenie, etc). Here is an example of the configuration.
- Customization: You can customize HolmesGPT with specific tools and runbooks to extend its capabilities. This is useful if you need the tool to access data that’s not normally available.
Once installed and configured, HolmesGPT can help with your Kubernetes troubleshooting. Let’s see some real-world scenarios in action.
Demo: Real-World Scenarios with HolmesGPT
Scenario 1: Debugging Kubernetes CrashLoopBackOff Error
In our first scenario we simulate a common Kubernetes issue: a pod stuck in a CrashLoopBackOff state. This error means the application running inside the pod is having a problem and is very generic and needs more troubleshooting steps.
- Setup: We create a Kubernetes namespace called demo and deploy a Flask application. The deployment includes a pod, a service and a config map with SSL certificates.
- Issue: After deploying the application the pod enters a CrashLoopBackOff state. This means the application is crashing and restarting.
- Using HolmesGPT: To troubleshoot, we ask HolmesGPT, “Why is my pod restarting?” HolmesGPT quickly investigates by running commands to find the existing pods that it should troubleshoot then checks logs, and analyzes the issue. It identifies the root cause as an expired SSL certificate.
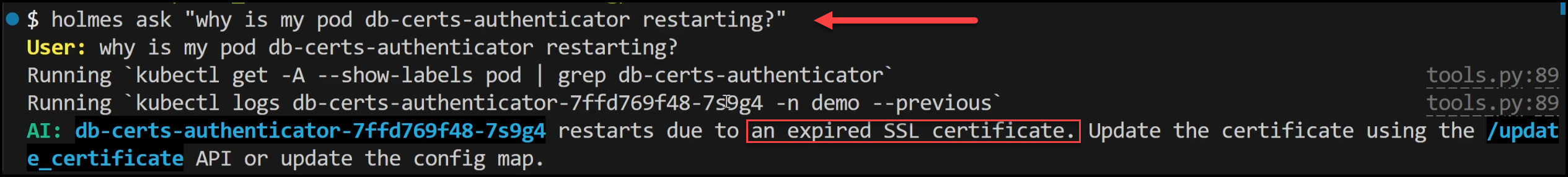
- Resolution: We update the SSL certificate with a new config map and apply it to the deployment. HolmesGPT confirms the issue is resolved by checking the logs again and verifying the application is running correctly.
Result: HolmesGPT finds the root cause of the issue, saving time and manual debugging. This scenario shows how HolmesGPT can help both experienced Kubernetes admins and newbies.
We can also integrate HolmesGPT with the Robusta SaaS using this article. Now let’s look at a few screenshots from the Robusta UI showing how we can arrive at the root cause for this issue.
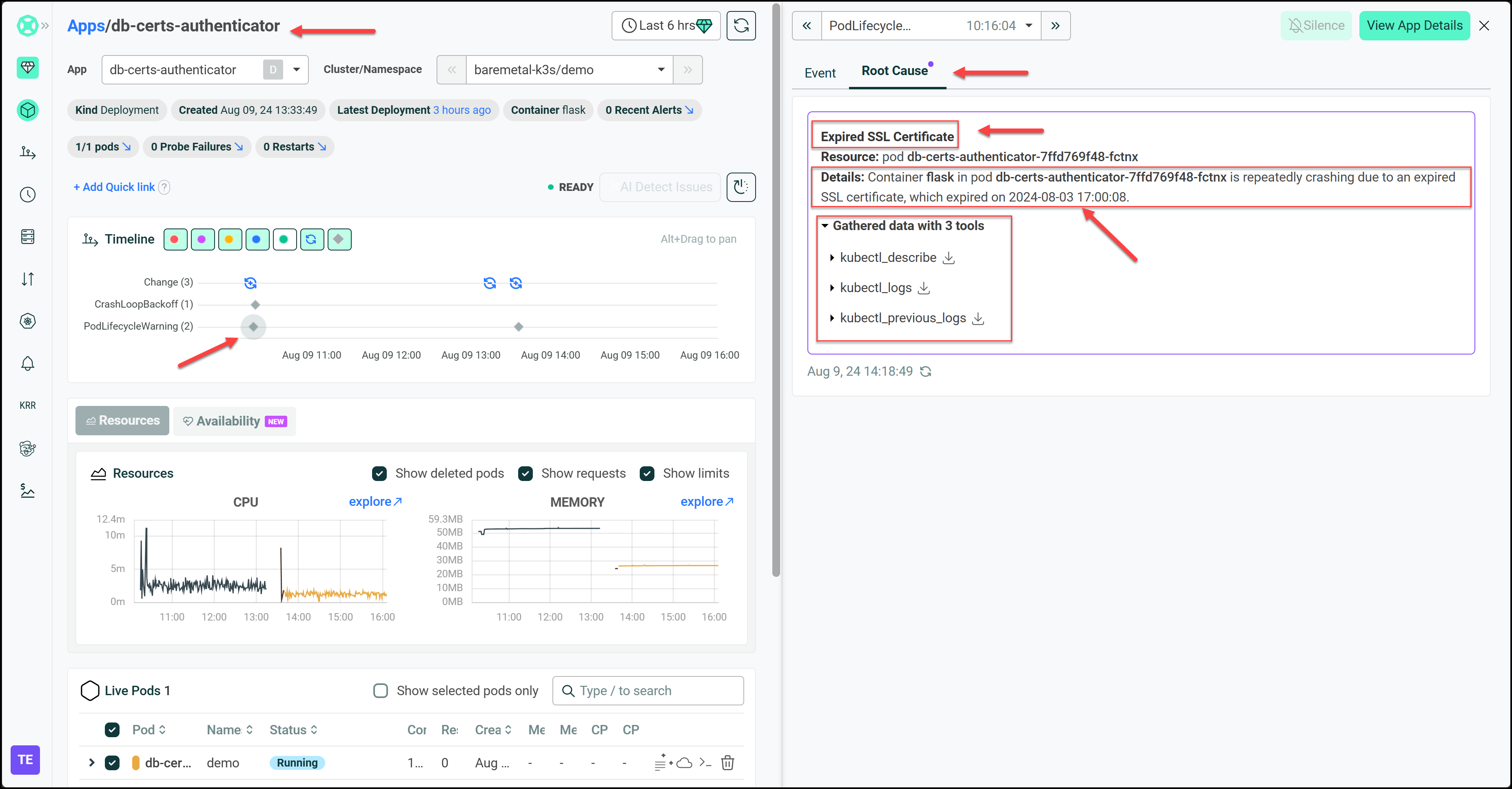
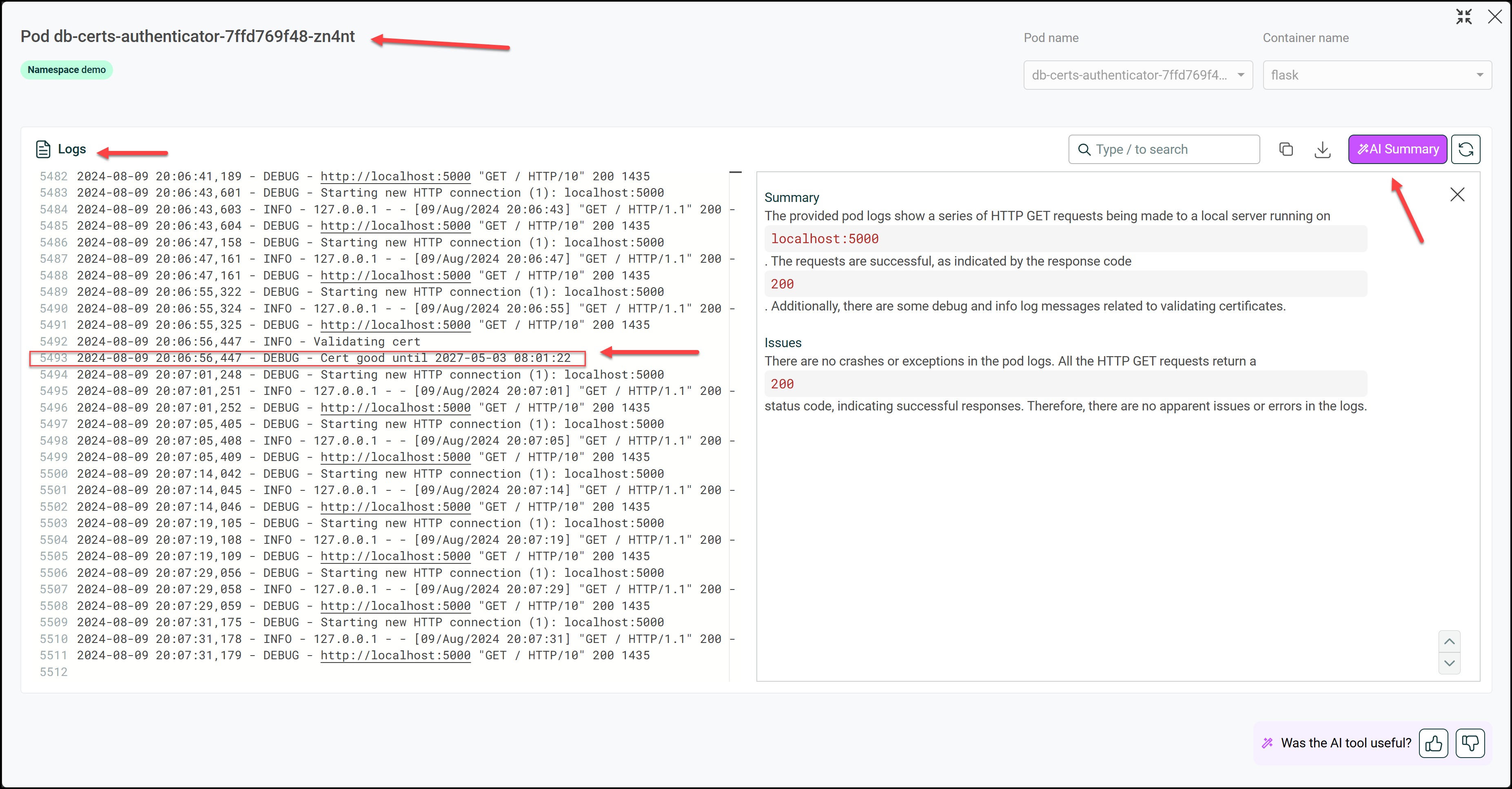
After fixing the error by applying a new certificate, we can investigate the pod’s logs and click on the AI Summary button to get a good summary of our logs in plain English.
Scenario 2: Troubleshooting Kubernetes Issues with Pending Resources
In the second scenario, we explore a situation where a pod remains in a pending state due to insufficient resources.
- Setup: We deploy a user profile application that requires specific resources, including CPU, memory, and an NVIDIA GPU.
- Issue: The pod stays in a pending state, unable to be scheduled on any of the worker nodes.
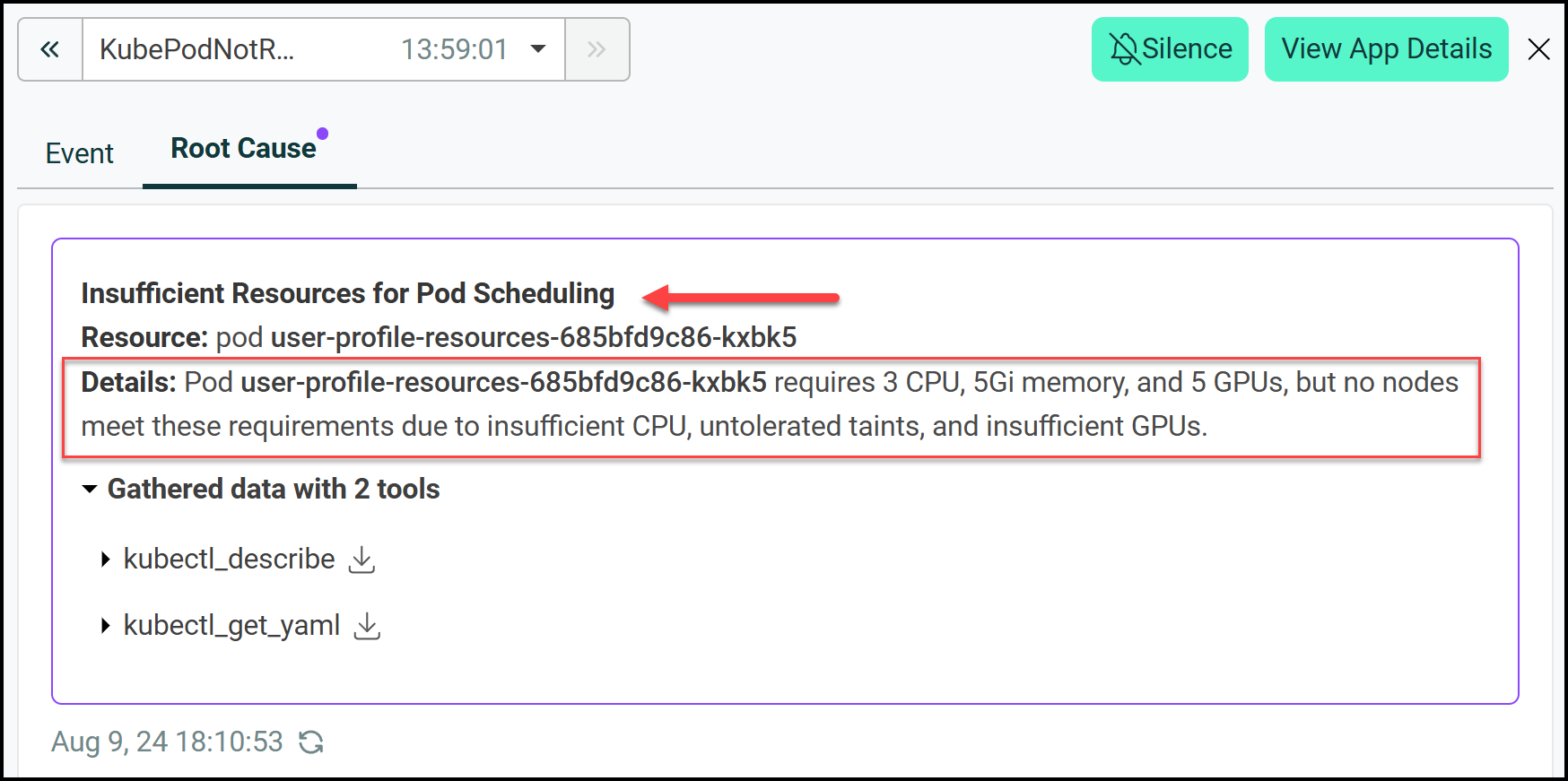
- Using HolmesGPT: We ask HolmesGPT to investigate the issue. It runs the kubectl describe pod command. HolmesGPT quickly identifies that the pod is pending due to insufficient CPU and GPU resources and taints on the master node.
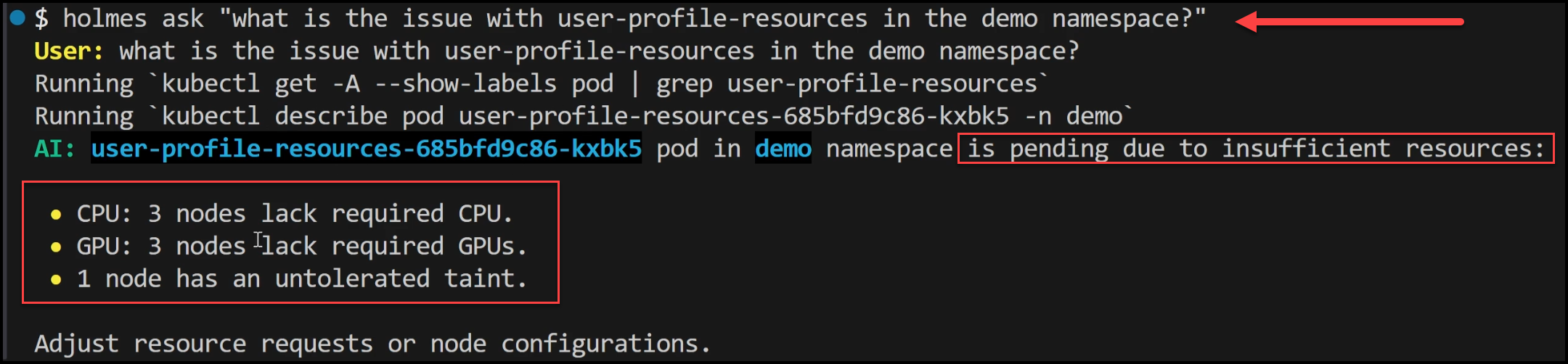
- Resolution: With the root cause identified, we can either scale the cluster to add more resources or adjust the resource requests in the deployment.
Result: HolmesGPT gives us a clear diagnosis of why the pod is pending so we can take action fast. This scenario shows how HolmesGPT can analyze resource related issues in Kubernetes environments.
Again we can see this in the Robusta UI:
Scenario 3: Node Selector Mismatch
The third scenario is a pod pending due to a node selector mismatch.
- **Setup: **We deploy a pod with a node selector that specifies a label that doesn’t exist on any of the nodes in the cluster.
- Issue: The pod can’t be scheduled because no nodes match the node selector label.
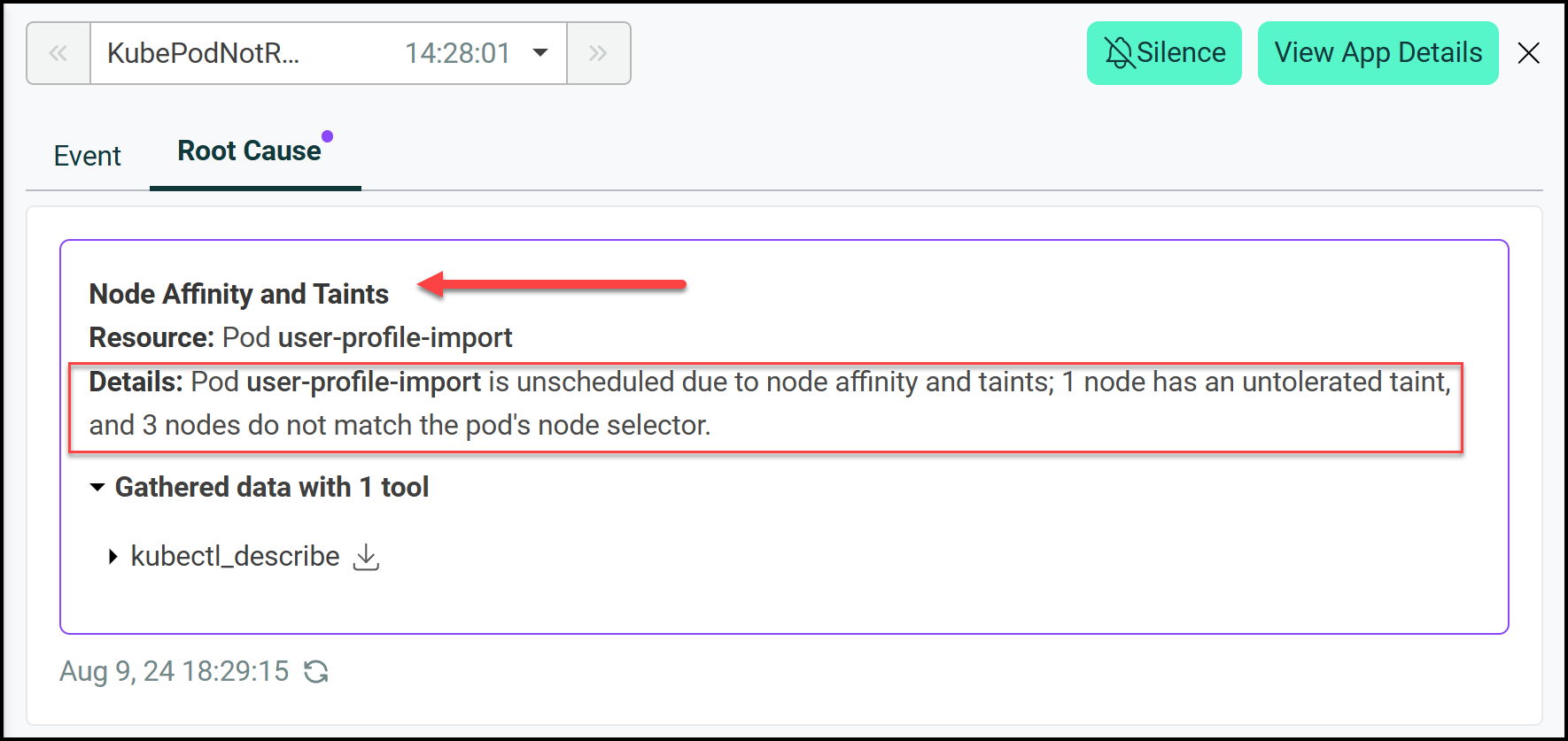
- Using HolmesGPT: We ask HolmesGPT why the pod is pending. It finds the node selector label in the deployment doesn’t match any available nodes so the pod is unscheduled.
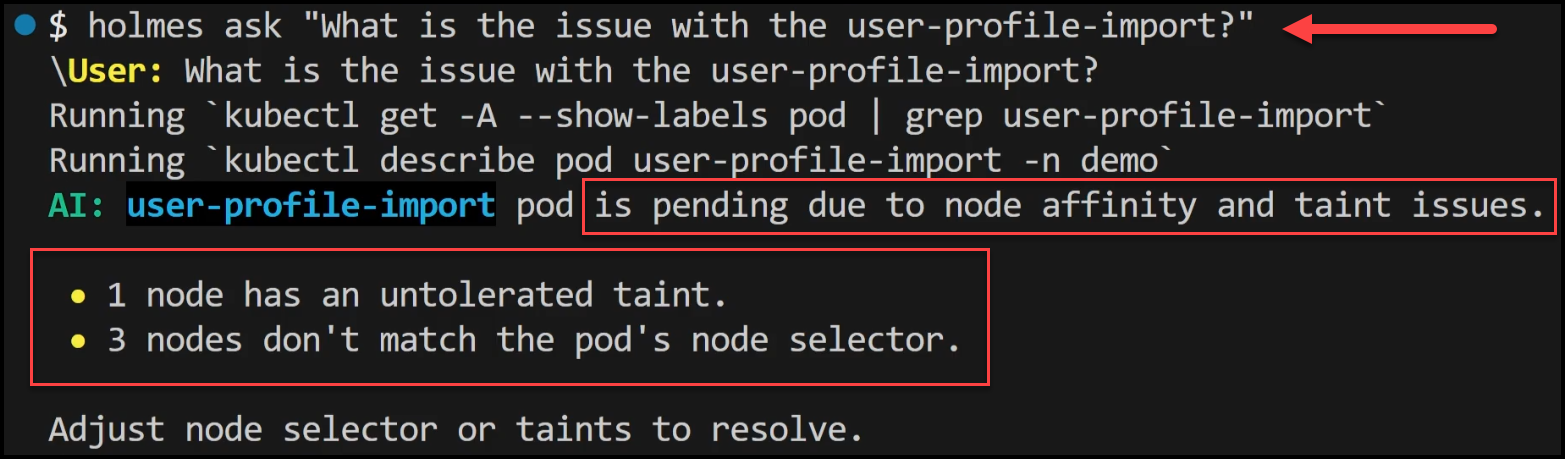
- Resolution: We either modify the node selector to match an existing node label or add the appropriate label to a node in the cluster.
Result: HolmesGPT finds the node selector mismatch and gives us a clear way to fix it. This scenario shows how HolmesGPT can diagnose configuration issues.
In the Robusta UI we can also see this:
Conclusion
Kubernetes troubleshooting is hard and time consuming, requires domain knowledge and patience. HolmesGPT makes it simpler by using AI to give you quick and accurate diagnosis of the issue in your cluster. Whether you have CrashLoopBackOff, pending resources or node selector mismatch HolmesGPT can help you get to the root cause fast.
HolmesGPT integrates with popular incident management tools and supports custom runbooks so it’s not just a troubleshooting tool but a DevOps assistant. As an open source and extensible tool it’s a great addition to any Kubernetes environment as clusters grow in size and complexity.
As Kubernetes continues to evolve and more companies adopt it, tools like HolmesGPT will become more and more important to keep critical applications reliable and performing. Whether you are a Kubernetes expert or just starting out, HolmesGPT will help you simplify your troubleshooting and keep your infrastructure running.
Try it out: Explore HolmesGPT on GitHub and see how it can transform your Kubernetes troubleshooting workflow.
Suggested Reading
- Crossplane Tutorial: Easy Steps to Master Kubernetes Clusters
- Build an Internal Developer Platform with GitOps: Part 1
- Create a Cloud Development Environment with Coder | Part 1/3
Code
Hi and Welcome!
Join the Newsletter and get FREE access to all my Source Code along with a couple of gifts.

